In 2020, 4,764 workers in the United States suffered fatal work injuries. More than 20% of those deaths occurred in the private construction industry.
With so many hazards at play, there are countless ways to get injured on the job. Dangerous environments, heavy equipment, and hazardous materials are just some of the risks. One way to mitigate these is by providing high-quality and continuous training for construction workers.
Here, we’ll go into 12 examples of training for construction workers to get you started on building out your ideal program to keep your staff safe.
12 examples of training for construction workers
1. OSHA training program
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) oversees safety in construction. OSHA plays a key role in ensuring workers’ safety by setting and enforcing rules. These rules cover crucial aspects like preventing falls, using secure equipment like scaffolds, and safeguarding against electrical hazards.
Sticking to OSHA’s rules is essential for construction firms to avoid penalties and prioritize worker safety. OSHA inspects workplaces, issues warnings for rule violations, and provides training to ensure staff know how to stay safe.
OSHA’s training is about more than just about teaching safety basics. It educates construction workers on safe material handling, injury prevention, and understanding specific work protocols. This training ensures everyone understands and follows OSHA’s guidelines, keeping the work environment secure.
OSHA’s training actively contributes to creating a safer construction zone, protecting workers, and ensuring strict adherence to safety protocols.
2. Excavation and trenching
One cubic yard of soil can weigh up to 3,000 pounds. With that in mind, it’s critical to have high-quality excavation and trenching training.
Construction worker training in excavation and trenching brings numerous benefits by enhancing safety awareness, identifying hazards, and preventing incidents related to these activities. This training is crucial to establishing a secure work environment, given that injuries from excavation and trenching can be more severe than other workplace accidents.
Excavation and trenching training equip employees with essential skills and awareness, minimizing the chances of incidents.
3. Fall prevention
Fall-related accidents are the leading cause of death in the construction industry.
Construction worker training in fall prevention provides essential knowledge for workers to identify and avoid common fall risks, utilize guardrails, personal fall arrest systems, and safety nets effectively, and mitigate potential fall dangers.
The focus of the training should also stress the importance of averting slips, trips, and falls, which can lead to strains, sprains, or even fatal consequences.
Fall prevention training is indispensable for ensuring the safety of construction workers and minimizing the occurrence of fall-related incidents in the workplace.
4. Hazard communication
Hazard communication training holds significant importance across various industries, especially in construction. Workers should be trained to identify and evaluate potential health risks at work and effectively communicate these hazards to colleagues.
Construction sites often expose workers to hazardous materials and chemicals, necessitating hazard communication training. As repeated exposure to such substances can cause severe health issues, workers must grasp safety procedures to handle and shield themselves from these hazards.
Construction businesses must implement comprehensive hazard communication training to shield workers and avoid legal liabilities. This training for construction workers not only educates on handling incidents involving hazardous materials but also instructs on responding to emergencies like spills, leaks, and worksite evacuations.
5. Power tools handling
Participating in power tool handling training within the construction sector brings various advantages, including heightened safety awareness, adherence to OSHA standards, and the prevention of workplace injuries.
This construction worker training empowers staff with knowledge of safely utilizing hand and power tools, minimizing common injuries, and recognizing associated hazards.
The training places significant emphasis on tool maintenance, selecting the right tools for specific tasks, proper operation, and the necessity of wearing suitable personal protective equipment (PPE). Employees gain proficiency and develop a deep respect for the tools they handle, promoting swifter and safer work practices.
6. Personal protective equipment (PPE)
PPE training empowers construction workers to determine what PPE is required for various tasks, including hard hats, hearing protection, eye and face guards, and more. It underscores the necessity of understanding construction hazards and utilizing PPE effectively to minimize risks.
OSHA standards mandate employers to furnish the most necessary PPE and provide training on its proper usage and maintenance. This training ensures workers comprehend the importance of wearing PPE, maintaining it adequately, and promptly reporting concerns.
7. Crane operation
Heavy machinery is present on every construction site. Construction workers and employers must know how to properly operate this equipment to avoid injury to themselves and others. Cranes can be found on most large construction sites. Because of their size and structure, a safety training course is a must.
Crane operation training typically covers topics such as crane safety, equipment operation, load handling, rigging, signaling, and compliance with OSHA regulations. Training may address the specific hazards associated with crane operations and the necessary precautions to prevent accidents and injuries.
8. Rigging
Severe injury or even death can occur due to falling objects or debris resulting from lifted materials or dropped loads. Worker positioning errors during a lift, gear malfunctions, or mistakes in rigging can lead to workers being struck by loads, causing unpredicted shifts or swings.
Rigging training programs explore various aspects of rigging, like stacking, storage, lifting techniques, rigging practices, equipment use, safe working loads, and rigging inspections. Emphasis is placed on thorough rigging equipment inspection, safe loading protocols, maintaining rigging records, and efficient signaling procedures.
9. Welding
Welding in construction exposes workers to risks like burns, electric shock, eye damage, noise, and toxic fume inhalation. Comprehensive safety training is crucial, covering protective gear use, safe material handling, proper ventilation, and recognizing health issues like respiratory problems or metal fume fever.
Understanding the differences between welding, soldering, and brazing is essential, with each method requiring specific safety measures to prevent accidents and ensure efficient work practices.
10. Harnessing
Working at heights, such as repairing roofs or installing windows, requires precise harnessing techniques for optimal safety. This requires comprehensive training on the proper use, inspection, and maintenance of safety equipment. Harnesses, ensuring balance while working aloft, and safe ascent and descent techniques are all necessary for a harnessing training program.
Equipment details, restraint systems, suspension systems, and the use of fixed or portable ladders in elevated work settings must also be covered.
Additionally, workers must gain insights into high fall hazards, preventive safety measures, and equipment maintenance practices, including inspection for defects, cleaning, and proper storage.
11. Scaffolding
OSHA requires employers to provide training to any employee who performs work on a scaffold. With many different scaffold types, the focus should be on suspension and supported scaffolds.
Training will focus on safety measures like guardrails, personal fall arrest systems, and strategies to minimize risks linked to scaffold work. Hazard recognition and understanding specific requirements for different scaffold types are also vital components.
12. Electrical safety
Training on electricity fundamentals is vital, encompassing the understanding of its basic concepts, potential hazards, and its impact on the human body. The focus lies in identifying, avoiding, and controlling electrical hazards to ensure worker safety by recognizing risks, implementing control measures, and comprehending the severity of these dangers.
Educating workers about potentially fatal electrical injuries, burns, arc flashes, and promoting safe electricity-related work practices is imperative. Familiarity with OSHA’s electrical standards and regulations plays a pivotal role in safeguarding employees from electric shock, electrocution, fires, and explosions.
Providing practical safety tips, emphasizing safe power-tool use, cord and wire safety practices, and encouraging the use of personal protective equipment are integral parts of mitigating electrical hazards. Workers must understand the significance of grounding, adhering to power tool requirements, and effectively controlling electrical hazards within construction environments, significantly ensuring worker safety.
Paper training manuals not cutting it?
Make training accessible anywhere with a powerful mobile learning app

FAQs
How do construction companies train their employees?
Construction companies use diverse methods and resources to train their workforce, ensuring safety, productivity, and adherence to industry standards. Some of the methods they use are:
- Easily accessible training materials
- Workshops and demonstrations
- Intensive safety orientation
- Visual training materials
- Specialized technical training
- Language training
- OSHA training
- Toolbox talks for reinforcing safety topics
Why is construction training important?
The construction industry has some of the greatest injury and fatality rates in the world. Interacting daily with heights, electricity, and heavy equipment means the chances for an accident to occur skyrocket. To mitigate risk, you must prioritize safety training for construction workers.
What type of OSHA training is available to a construction worker?
Outreach training, either 10 or 30-hour classes, covers basic hazard awareness courses for workers and is taught by OSHA-certified instructors.
What is the Georgia Construction Ready Program?
The Georgia Construction Ready Program provides comprehensive construction training and job placement, allowing individuals to pursue fulfilling careers in the construction industry.
Make construction worker training accessible
The subjects mentioned above are just a few that your training for construction workers program should have to ensure the safest work environment possible. OSHA is a key component in the construction industry. So much so that it requires every constriction staff member to take a 10 or 30-hour OSHA workplace safety training class. In addition to this requirement, all companies should offer ongoing safety training for construction workers.
What is the easiest and most efficient way to do that?
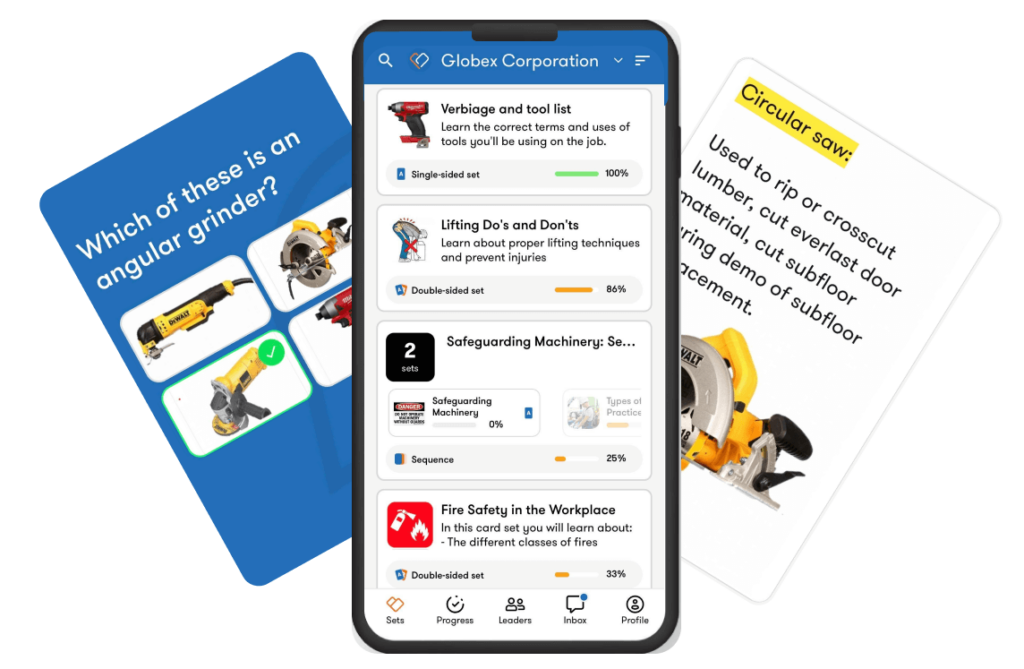
Provide easy access to training on the go with TalentCards, a mobile training platform built for employees in the field. Your staff can complete required training, access previous learning when questions arise, and stay compliant on the go. Training for construction workers has never been easier.
Key takeaways
- OSHA plays a vital role in ensuring construction worker safety by setting and enforcing rules, covering crucial aspects such as fall prevention, equipment safety, and electrical hazards. Compliance with OSHA regulations is crucial to avoid penalties and prioritize worker safety.
- Training significantly enhances safety awareness, helps identify hazards, and prevents incidents in construction workplaces. It empowers workers with crucial skills, knowledge, and protocols to minimize the risk of injuries or accidents, particularly in high-risk areas like excavation, fall prevention, and electrical safety.
- Providing easily accessible training materials, conducting workshops and demonstrations, intensive safety orientation, and specialized training tailored to specific hazards ensure a well-rounded and effective training program.
Want to learn how you can train construction teams right form their smartphones?
Let’s talk.